| Version 8 (modified by , 16 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
Cosimulation using SoCLib components and RTL models
You may use CABA models together with RTL models using ModelSim. This needs the following parts:
- a set of SystemC models
- a set of Verilog/VHDL models
- glue wrappers where needed, exporting a RTL model to SystemC or SystemC to RTL (scgenmod to export RTL model to SystemC but this is not covered in this guide)
- a SystemC clock driver (we had some issues with vhdl clock driver), i.e. a module bagotting clock signal
SystemC modules are SoCLib ones and are usually compiled with SoCLib-cc. They come with pure-c++ dependancies which must be linked together with the modules.
Due to its simulator core design, ModelSim has to compile SystemC
modules a special way, and has a dedicated tool to compile SystemC/C++
files: sccom.
Soclib-cc has three main jobs:
- Select modules and dependancies from a platform description file,
- Explicitly instantiate C++ templates,
- Call the C++ compiler. Only this step is implemented in
sccom.
The flow is as in the picture:

soclib-cc handles most of this automagically if correctly configured. This guide explains how to set things up.
Moreover, the C/C++ only dependancies are not
directly compileable with the dedicated ModelSim tool, but can be
injected at the last time, for the linkage phase (sccom -link).
How to configure SoCLib-cc to call ModelSim compiler driver
Sometimes, the C++-only dependencies of SystemC modules need to Know about SystemC types. Therefore, SystemC includes must be available.
soclib-cc needs new configuration sections for
- the compiler used by sccom
- the path to ModelSim's SystemC implementation
- used flags
- object file names pattern in sccom work directory
For all these, we must create 3 new configurations in soclib-cc's configuration file:
- a compiler
- a SystemC library
- a build environment
# Definition of the compiler used for ModelSim-usable SoCLib components.
# We use sccom for components compilation and linkage, gcc/g++ for utilities
config.modelsim_toolchain = Toolchain(
parent = config.toolchain,
# Must use this.
tool_map = {
'SCCOM_CC':'sccom',
'SCCOM_CXX':'sccom',
'CC':'/users/soft/mentor/modelsim-6.5c/modeltech/bin/gcc',
'CXX':'/users/soft/mentor/modelsim-6.5c/modeltech/bin/g++',
'CC_LINKER':'sccom',
'CXX_LINKER':'sccom',
},
# Modelsim cant do parallel builds :'(
max_processes = 1,
# No cflags are needed, sccom forces them
cflags = ['-m32'],
# Special features, it has a -link invocation needed at end...
libs = ['-link'],
)
# Definition of the ModelSim SystemC implementation. Must modify the
# path according to the ModelSim current installation.
config.libsystemc_modelsim = Library(
name = 'systemc',
# This special vendor attributes enables some quirks in soclib-cc
vendor = 'modelsim',
# This is the path of the produced .o files when compiled with sccom.
# You have to try it by hand, and adapt
sc_workpath = "work/_sc/linux_gcc-4.1.2",
# Empty useless variables
libs = [],
# cflags have to be deducted from actual invocation
# Try using sccom -v by hand
cflags = ['-I/users/soft/mentor/modelsim-6.5c/modeltech/include/systemc',
'-I/users/soft/mentor/modelsim-6.5c/modeltech/include',
'-I'+config.path+'/soclib/lib/include'],
)
# Definition of a new build environment, which can be referenced with 'soclib-cc -t'
config.modelsim = BuildEnv(
parent = config.build_env,
toolchain = config.modelsim_toolchain,
libraries = [config.libsystemc_modelsim],
# Where temporary files lies, beware that if you set a global path,
# you'll need a mechanism to make user-unique directories.
repos = "/tmp/",
)
SystemC modules in ModelSim limitations
All modules that may be used from the outside of the SystemC-part
(from RTL or from GUI) have to be declared with a special macro
(SC_MODULE_EXPORT).
There is no sc_main() function in modelsim-based simulators. The top
module must be a sc_module with no interfaces. This probably needs a
rewrite of your netlists.
If you use DSX-generated netlists, this is done transparently.
Usage
Now we configured soclib-cc, we can compile a complete SystemC system.
Let's have an example system with two basic components communicating through a fifo.
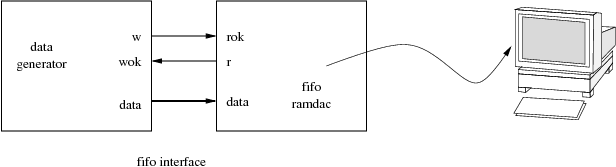
We'll use
- SoCLib SystemC Fifo Ports,
- a VHDL
fifo_gencomponent, - a VHDL-SystemC
fifo_gen_wrapperwrapper, - a SystemC
fifo_wrapperhosting a pure-C++.
This basic system has to be modeled as the following tree:
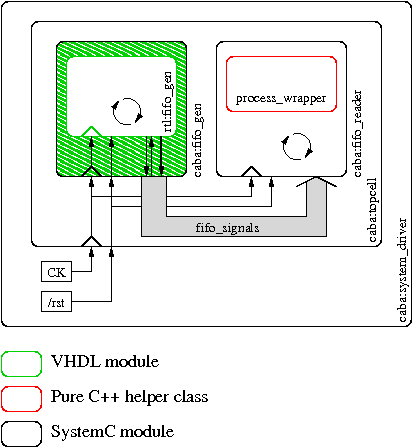
It contains:
fifo_gen- The VHDL component writing to the Fifo
fifo_gen_wrapper-
The VHDL/SystemC wrapper to export
fifo_gento the SystemC world fifo_reader- A SystemC component reading from the fifo
topcell- A SystemC component implementing the topcell
system_driver-
A SystemC component controlling
resetandclocksignals
In order to simulate this system we need to:
- Reset the work directory, to make sure,
$ rm -rf work transcript modelsim.ini fifo_gen_wrapper/fifo_gen.h vsim.wlf
- Initialize modelsim
workdirectory,$ vlib work $ vmap work work
- Compile the VHDL module with vcom.
$ vcom fifo_gen/fifo_gen.vhd
- Generate the SystemC wrapper of the
fifo_genVHDL module withscgenmod$ scgenmod -sc_uint -bool fifo_gen > fifo_gen_wrapper/fifo_gen.h
- Compile the SystemC system driver with soclib-cc, all dependancies are pulled with it.
.sdmetadata are needed (even for the VHDL/SystemC wrapper), see in tarball.$ soclib-cc -1 caba:system_driver -t modelsim -v -o sccom-link.o
- Open modelsim with the platform
$ vsim -novopt -sclib work system_driver
See the attached tarball for the complete example
Attachments (7)
- cosim-pf1.fig (3.4 KB) - added by 16 years ago.
- cosim-pf1.png (9.9 KB) - added by 16 years ago.
-
cosim.tar.bz2 (3.5 KB) - added by 16 years ago.
Complete example
- cosim-pf2.png (9.4 KB) - added by 16 years ago.
- soclib-cc-modelsim-flow.png (14.4 KB) - added by 16 years ago.
- soclib-cc-modelsim-flow.fig (5.6 KB) - added by 16 years ago.
- cosim-pf2.fig (4.4 KB) - added by 16 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip

